1. Lab-Grown Meat
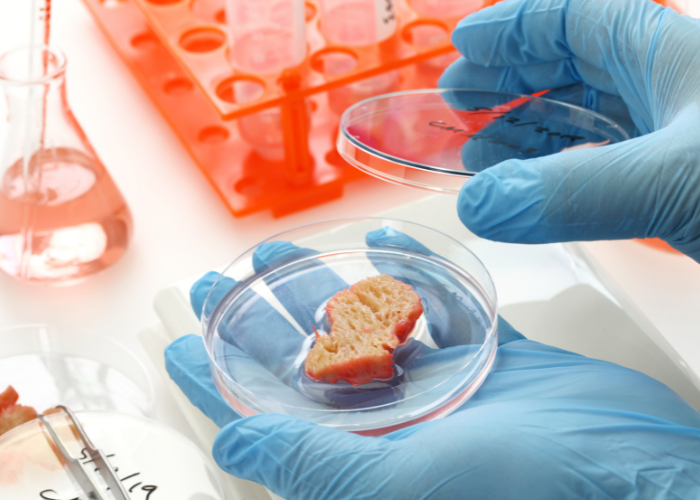
Cultured or lab-grown meat is produced by culturing animal cells in a laboratory instead of raising and slaughtering animals. This innovative approach has the potential to significantly reduce the environmental impact of meat production, as well as address ethical concerns associated with traditional livestock farming.
2. Vertical Farming
Vertical farming involves growing crops in vertically stacked layers, often in controlled indoor environments. This method of farming maximizes the use of space, reduces the need for pesticides, and allows for year-round crop production. It is especially promising for urban areas with limited arable land.
3. Edible Insects
Insects are a rich source of protein, vitamins, and minerals, and they require less land, water, and feed than traditional livestock. Many cultures around the world already consume insects, and as the demand for sustainable protein sources grows, edible insects are likely to become more mainstream.
4. Plant-Based Proteins
Plant-based proteins, made from ingredients like soy, peas, and lentils, are becoming increasingly popular as an alternative to animal-based proteins. These products not only cater to vegetarians and vegans but also to those looking to reduce their meat consumption for health or environmental reasons.

5. Food Waste Reduction Technologies
Approximately one-third of the food produced globally is wasted. Innovations in packaging, storage, and transportation are helping to reduce food waste and ensure that more food reaches those who need it. For example, smart packaging that changes color when the food inside is spoiling, or apps that connect consumers with surplus food from restaurants and grocery stores.
6. Personalized Nutrition
Advancements in genetics and data analysis are enabling more personalized approaches to nutrition. By analyzing an individual's genetic makeup, lifestyle, and health history, it is possible to create personalized diet plans that optimize health and prevent disease.
7. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Agriculture
AI is being used to optimize farming practices, from planting and irrigation to pest control and harvesting. For example, drones equipped with sensors can monitor crop health and environmental conditions in real-time, allowing farmers to make informed decisions and maximize yields.
8. 3D Food Printing
3D food printing involves layer-by-layer printing of edible ingredients to create food products. This technology allows for the customization of food in terms of shape, texture, and nutritional content, and has potential applications in personalized nutrition, foodservice, and space travel.
9. Alternative Sweeteners
Excessive sugar consumption is a major public health concern. Alternative sweeteners, derived from sources like stevia, monk fruit, and allulose, offer a way to satisfy our sweet tooth without the negative health effects associated with sugar.
10. Aquaponics and Hydroponics
Aquaponics is a system that combines aquaculture (raising fish) with hydroponics (growing plants in water without soil). The fish waste provides nutrients for the plants, while the plants help to filter and purify the water. This creates a closed-loop, sustainable system for growing both fish and plants.
These innovations are just a glimpse into the future of food. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more groundbreaking solutions to address the challenges of feeding a growing global population while minimizing the environmental impact. Embracing these innovations will be key to creating a more sustainable and nutritious food system for all.
